| Title | Spectroscopic Study of a DNA Brush Synthesized in situ by Surface Initiated Enzymatic Polymerization |
| Publication Type | Journal Article |
| Year of Publication | 2013 |
| Authors | Khan, MN, Tjong, V, Chilkoti, A, Zharnikov, M |
| Journal | The Journal of Physical Chemistry B |
| Volume | 117 |
| Issue | 34 |
| Pagination | 9929–9938 |
| Date Published | 07/2013 |
| ISSN | 1520-5207 |
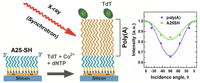
| Abstract | We used a combination of synchrotron-based X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and angle-resolved near-edge X-ray absorption fine structure (NEXAFS) spectroscopy to study the chemical integrity, purity and possible internal alignment of single-strand (ss) adenine deoxynucleotide (poly(A)) DNA brushes. The brushes were synthesized by surface-initiated enzymatic polymerization (SIEP) on a 25-mer of adenine self-assembled monolayer (SAM) on gold (A25-SH), wherein the terminal 3-OH of the A25-SH serve as the initiation sites for SIEP of poly(A). XPS and NEXAFS spectra of poly(A) brushes were found to be almost identical to those of A25-SH initiator, with no unambiguous traces of contamination. Apart from the well-defined chemical integrity and contamination-free character, the brushes were found to have a high degree of orientational order, with an upright orientation of individual strands, despite their large thickness up to ~55 nm, that corresponds to a chain length of at least several hundreds nucleotides for individual ssDNA molecules. The orientational order exhibited by these poly(A) DNA brushes, mediated presumably by base stacking, was found to be independent of the brush thickness as long as the packing density was high enough. The well-defined character and orientational ordering of the ssDNA brushes make them a potentially promising system for different applications. |
| DOI | 10.1021/jp404774x |
| Short Title | J. Phys. Chem. B |